|
JSON代表JavaScript对象符号。它是一个独立的数据交换格式,是XML的最佳替代品。本章介绍了如何解析JSON文件,并从中提取所需的信息。
Android提供了四个不同的类来处理JSON数据。这些类分别是:JSONArray,?JSONObject,JSONStringer?和?JSONTokenizer.
第一步是确定感兴趣的JSON数据的字段,例如。在JSON给我们下面感兴趣的数据:温度
{
"sys":
{
"country":"GB",
"sunrise":1381107633,
"sunset":1381149604
},
"weather":[
{
"id":711,
"main":"Smoke",
"description":"smoke",
"icon":"50n"
}
],
"main":
{
"temp":304.15,
"pressure":1009,
}
} |
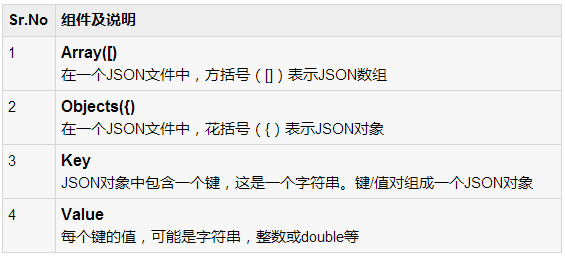
JSON 元素
JSON文件包含许多组件。这里是表定义一个JSON文件及其说明的组件:
JSON - 解析
解析一个JSON对象,我们将创建一流的 JSONObject 对象,并指定包含JSON数据给它一个字符串。其语法是:
String in; JSONObject reader = new JSONObject(in); |
最后一步是解析JSON。一个JSON文件由不同的对象有不同的键/值对等,这样JSONObject有一个单独的函数用于解析每个JSON文件的组成。它的语法如下:
JSONObject sys = reader.getJSONObject("sys");
country = sys.getString("country");
JSONObject main = reader.getJSONObject("main");
temperature = main.getString("temp"); |
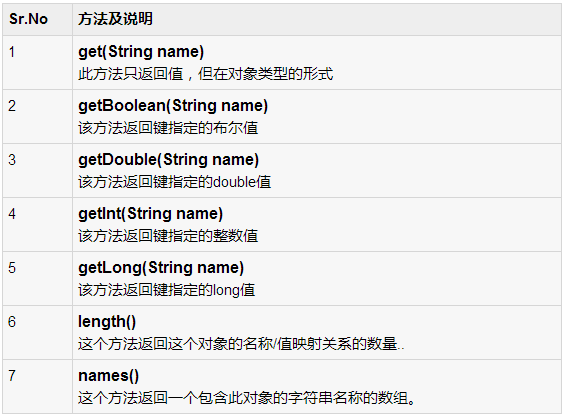
getJSONObject返回JSON对象的方法。形式返回指定键的字符串值的方法。
除了这些方法,还有更好的解析的JSON文件所提供的此类其他方法。这些方法如下:
例子
这里有一个例子演示如何使用的JSONObject类。它创建了一个基本的天气应用程序,允许用户从谷歌API的天气JSON解析并显示结果。
为了试验这个例子,可以在实际设备或模拟器运行此。
以下是修改后的主活动文件?src/com.yiibai.jsonparser/MainActivity.java. 的内容?
package com.example.jsonparser;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String url1 = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=";
private EditText location,country,temperature,humidity,pressure;
private HandleJSON obj;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
location = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1);
country = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2);
temperature = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText3);
humidity = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText4);
pressure = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText5);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items
//to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
public void open(View view){
String url = location.getText().toString();
String finalUrl = url1 + url;
country.setText(finalUrl);
obj = new HandleJSON(finalUrl);
obj.fetchJSON();
while(obj.parsingComplete);
country.setText(obj.getCountry());
temperature.setText(obj.getTemperature());
humidity.setText(obj.getHumidity());
pressure.setText(obj.getPressure());
}
} |
以下是?src/com.yiibai.jsonparser/HandleXML.java.的内容
package com.example.jsonparser;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserFactory;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
public class HandleJSON {
private String country = "county";
private String temperature = "temperature";
private String humidity = "humidity";
private String pressure = "pressure";
private String urlString = null;
public volatile boolean parsingComplete = true;
public HandleJSON(String url){
this.urlString = url;
}
public String getCountry(){
return country;
}
public String getTemperature(){
return temperature;
}
public String getHumidity(){
return humidity;
}
public String getPressure(){
return pressure;
}
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public void readAndParseJSON(String in) {
try {
JSONObject reader = new JSONObject(in);
JSONObject sys = reader.getJSONObject("sys");
country = sys.getString("country");
JSONObject main = reader.getJSONObject("main");
temperature = main.getString("temp");
pressure = main.getString("pressure");
humidity = main.getString("humidity");
parsingComplete = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void fetchJSON(){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
URL url = new URL(urlString);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setReadTimeout(10000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setConnectTimeout(15000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setDoInput(true);
// Starts the query
conn.connect();
InputStream stream = conn.getInputStream();
String data = convertStreamToString(stream);
readAndParseJSON(data);
stream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
static String convertStreamToString(java.io.InputStream is) {
java.util.Scanner s = new java.util.Scanner(is).useDelimiter("A");
return s.hasNext() ? s.next() : "";
}
} |
以下是修改XML文件?res/layout/activity_main.xml. 的内容
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:text="@string/location"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:ems="10" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_marginTop="68dp"
android:text="@string/country"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_marginTop="19dp"
android:text="@string/temperature"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:text="@string/humidity"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_marginTop="21dp"
android:text="@string/pressure"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView3"
android:ems="10" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText2"
android:ems="10" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText1"
android:ems="10" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/textView5"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText4"
android:ems="10" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText1"
android:onClick="open"
android:text="@string/weather" />
</RelativeLayout> |
以下是?res/values/string.xml. 的内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">JSONParser</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string>
<string name="location">Location</string>
<string name="country">Country:</string>
<string name="temperature">Temperature:</string>
<string name="humidity">Humidity:</string>
<string name="pressure">Pressure:</string>
<string name="weather">Weather</string>
</resources> |
以下是?AndroidManifest.xml?文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.yiibai.jsonparser"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.yiibai.jsonparser.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest> |
让我们试着来运行修改JSONParser应用。安装程序在AVD并启动它,如果一切设置和应用程序都没有问题,它会显示以下仿真器窗口:
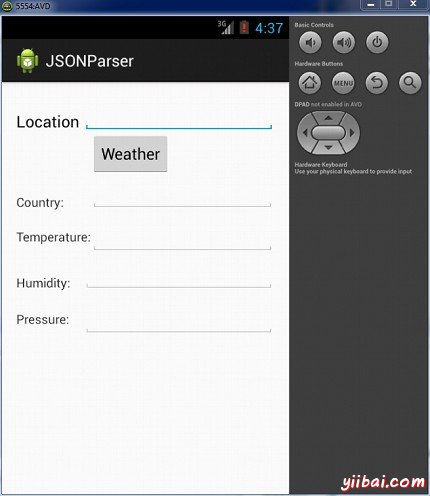
现在,需要做的是在位置字段中输入的任何位置。举例来说,我已经进入了纽约。按下"weather?"按钮,当输入的位置。下面的屏幕会出现在AVD中:
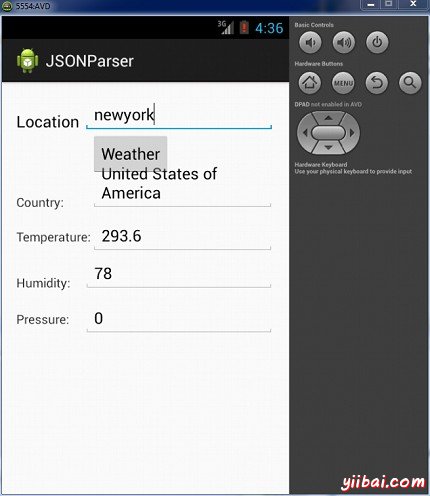
现在,当按下"weather"按钮,应用程序将联接谷歌天气API,并会请求需要的JSON文件,并解析它。如果输入的为:纽约以下文件将返回:
伦敦谷歌的天气API温度
请注意,这个温度是开尔文,所以如果你想将其转换成更易于理解的格式,必须把它转换成摄氏度。
|
